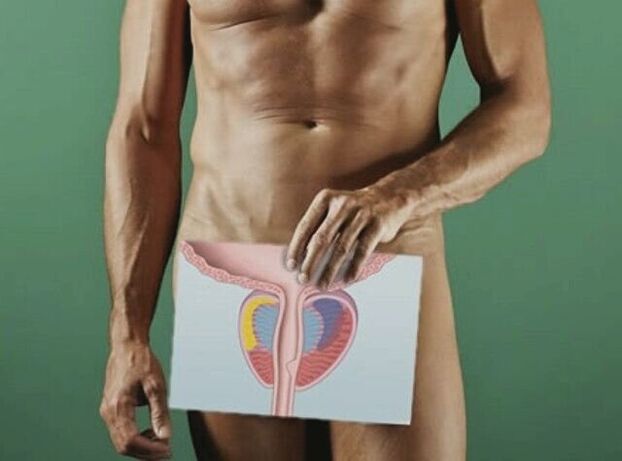
The term "prostatitis (microbial code 10-41)" refers to inflammatory processes that occur in the tissues of the prostate and lead to pain, difficulty urinating, frequent need to go to the bathroom, decreased libido. According to various statistics, the disease mainly affects men of reproductive age, that is, 25 to 50 years old. Depending on the characteristics of the symptom complex and the degree of damage to the gland, two forms of prostatitis are distinguished - acute and chronic.
According to the MCB coding, prostatitis in the chronic form is assigned a value of 41. 1, for the acute form, the figure 41. 0 is used. the primary diagnosis is made by visually examining the patient and studying the history. For confirmation, additional techniques are used: ultrasound and laboratory methods.
General characteristics and classification
One in every third of the representatives of the strong half of humanity knows what prostatitis is, presenting itself in various forms, because this disease, caused by inflammation of the prostate, is one of the most common pathologies of the male genital area. The disease is manifested by characteristic symptoms: pain, burning sensation, aggravated by the act of urinating, decreased sexual activity, frequent need to go to the bathroom.
Prostatitis in men is a consequence of the prostate's defeat by infectious agents that enter its tissues through the reproductive organs or systemic circulation. Even reasons like a common cold or bronchitis can trigger an inflammatory process. Most of the time, this happens in the context of factors favorable to the spread of the infection, among which, in the first place, is called weakened immunity.
To obtain the average indicators, there is a statistical coding of prostatitis mkb 10, which allows an objective assessment of the situation regarding the incidence of the male half of the population. Chronic prostatitis mkb 10 has a code 41. 1, which is attributed to an illness that lasts six months or more. Furthermore, the classification of the international code ICB 10 xp prostatitis characterizes this form of the disease as difficult to treat.
Acute prostatitis mkb code 10 is assigned a slightly different code - 41, 0. This form of the disease is recognized as a very mild therapy used and occurs in the context of pronounced symptoms of the disease. There is also code 41. 2. The indicator provided usually designates a disease associated with the formation of an abscess in the prostate. It is important to know that the diagnosis of chronic prostatitis recommends that the man undergo treatment at least once every six months and visit a specialist regularly.
predisposing factors
The probability of acute and chronic prostatitis in men increases significantly in the context of the negative action of predisposing factors. The following reasons can become something of a catalyst for inflammatory processes that affect prostate tissues:
- Stagnant phenomena, characterized by impaired blood flow, and arising in the context of a sedentary lifestyle, low sexual activity, overweight.
- Systematic hypothermia of the body, caused, for example, by the peculiarities of work.
- Injuries, regardless of the nature and time elapsed since the injury.
- Infectious and viral diseases of the genital area, including sexually transmitted diseases.
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases of other systems and organs, for example, bronchitis, purulent tonsillitis and many others.
As an additional predisposing factor, practical medicine also cites digestion problems, expressed in the appearance of systematic constipation. Thus, an inadequate approach to nutrition can also have an indirect effect on the occurrence of prostate inflammation.
Important! Timely elimination or reduction of the influence of negative factors is the most reasonable and effective method of preventing prostatitis in men.
Clinical condition
Probably many people know what prostatitis is in several ways. But not everyone is aware that the classic signs of this unpleasant disease can change significantly depending on the stage and form of the pathology:
- Catarrhal prostatitis. The disease is characterized by the appearance of pain in the perineum, groin, frequent need to go to the bathroom.
- Follicular prostatitis. The painful syndrome becomes more intense, difficulties in urinating occur, and a false desire to go to the bathroom may appear.
- Parenchymal prostatitis. Intense pain syndrome, aggravated by the act of urinating or defecating, there is often delay in the flow of urine, false desire to go to the bathroom, high temperature, chills, weakness, fatigue.
The course of chronic prostatitis is accompanied by the appearance of nearly all of the signs listed above, but the symptoms become more exhausted. It is important to emphasize that the acquisition of the chronic form of the disease is quite rare in a context of exacerbations. Mainly, this form of the disease develops in men gradually, under the influence of inflammatory processes resulting from an infectious lesion of the tissues of the prostate. Its main symptoms are:

- Dysuric syndrome. In the context of the negative influence of inflammatory processes, the prostate significantly increases in volume, leading to compression of the ureter. This pathology is the main reason for the appearance of a frequent urge to urinate, including false and painful sensations.
- Pain syndrome. The prostate itself is devoid of nerve endings, respectively, the painful sensations in prostatitis are a consequence of the spread of inflammatory processes and damage to nerve fibers adjacent to the prostate from Organs pelvic organs.
- Sexual dysfunctions. Prostate diseases are characterized by the appearance of various disorders of a sexual nature. Most men complain of a decrease in the intensity and brightness of sensations received during intercourse; in the early stages of disease development, decreased libido and lack of erection are possible. For advanced forms of pathology, impotence is characteristic.
You need to know that the development of prostatitis is often accompanied by disturbances in the patient's psycho-emotional history. The man is more irritated, the development of depressive states, nervous crises is possible.
Prostatitis is associated with a characteristic clinical picture, which greatly simplifies timely diagnosis. The main diagnostic methods are the rectal examination performed by a specialist manually, the ultrasound examination, as well as the collection of urine and prostatic secretions for laboratory analysis.
treatment methods
The treatment of prostatitis, whose methods will be more suitable in a given clinical case, is determined exclusively by the attending physician, based on research results, the patient's physiological characteristics, the form and degree of development of the disease. Most of the time, complex therapy methods are used, including medication intake, physical therapy methods, folk remedies, as well as diet correction.
Treatment of the chronic form
Chronic prostatitis is a particularly unpleasant disease, its treatment is fraught with a series of problems and difficulties, making it almost impossible to eliminate the disease completely. However, the use of competent therapy will allow achieving stable and lasting remission, in addition to eliminating the main symptoms of the disease and significantly improving the quality of life. The main treatment methods are:
- Medical treatment. The selection of medications is made according to a scheme elaborated individually by a specialist, mainly antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs. To eliminate pain in the early stages of treatment, the use of analgesics is allowed.
- Physiotherapy. To stimulate regenerative processes and increase the effectiveness of the active components of drugs, along with drugs, physical therapy methods are used, such as laser therapy, magnetotherapy, electrophoresis.
- Massage. One of the most effective methods of treating prostatitis, regardless of its form and stage, is prostate massage. The procedure helps to relieve inflammation, eliminates the phenomena of stagnation, pain. The massage, as a rule, is performed by a specialist in a medical institution, however, subject to the mandatory mastery of medical techniques, it is allowed to do it at home.
- Immunomodulatory therapy. Therapy for chronic prostatitis involves mandatory ingestion of immunomodulating drugs that increase immune strength and overall body tone. To eliminate this unpleasant disease, the selection of medications should be based on the prescriptions of the treating physician.
In addition, the treatment provides for the mandatory refusal of the patient to existing bad habits, correction of diet and daily regimen. Including a range of products fortified with useful vitamins and trace elements in the usual menu will help to strengthen the body. Moderate physical activity is also an important measure. Physical activity will help prevent stagnation phenomena and normalize blood and lymph flow.
Important! Treatment of prostatitis can only be carried out under the supervision of a specialist. Self-administration of medications or the use of other techniques can lead to negative consequences and deterioration of the patient's condition.
Treatment during an exacerbation
Competent treatment of acute prostatitis, subject to the timely use of appropriate therapy, allows you to completely get rid of the disease and normalize prostate function. It is important to know that this form of the disease tends to become chronic and therefore treatment should be carried out when the primary symptoms appear.
Therapy for acute prostatitis includes the use of medications with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. As a supplement, physiotherapy methods, massage and a mild diet can be used. If the disease evolves in the context of the formation of purulent abscesses, surgical intervention is necessary in order to open the capsule, remove purulent masses and eliminate the focus of inflammation.
possible complications
Lack of treatment for the acute and chronic forms of prostatitis can lead to the development of complications. In the context of the course of inflammatory processes in the form of exacerbation, there is a risk of formation of purulent abscesses in the tissues of the prostate, that is, a kind of capsule with purulent content. The condition of the patient in such a situation worsens drastically, there is a delay in the output of urine, severe pain syndrome, high fever, chills.
The most common complications of chronic prostatitis include the risk of developing inflammatory processes that affect the bladder and genital tissues. Furthermore, in the vast majority of cases, the disease is accompanied by sexual dysfunction, leads to a decrease in libido, various disorders of the reproductive system and, in the most serious cases - impotence. It is almost impossible to completely cure these pathologies.
For the cure of the disease, prevention of complications and the acquisition of chronic or advanced prostatitis, it is important to take the necessary measures in a timely manner. It is necessary to consult a specialist to identify the causes of the discomfort and to prescribe the appropriate therapy when the first symptoms of the illness appear. It is the ignorance of the first alarms and the omission of the necessary time that leads to the serious complications of the disease.