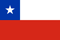
One of the most dangerous complications of acute prostatitis can be an abscess of the prostate gland. This is a focal purulent inflammation, in which body temperature can rise to 40 degrees. The signs of the abscess are acute intensive pain and difficult urination. In the absence of medical assistance, the swelling of glandular tissues develops and the urethra lumen is completely blocked.
Prostatitis is the most common urological pathology in men of reproductive age. According to research, every third of them at least once in their life has experienced symptoms that can be interpreted as inflammation of the prostate gland. The main cause of the development of bacterial prostatitis is an infection, however, only in the case of acute prostatitis, the infection leads to a marked inflammation of the prostate gland, which is explained by the anatomical characteristics of the male body structure.
In the chronic form of prostatitis, the infection can also be the cause, the inflammation trigger mechanism, but inflammation of the prostate gland, which requires treatment, can only develop against the background of other factors:
- Extended hypothermia of a different nature: It can be a bath in an ice hole or sitting on cold stones, etc. ;
- Sedentary lifestyle (sedentary), leading to blood stagnation, which can also cause inflammation;
- Irregular sex life: refers to excessive abstinence and excessive activity;
- Transferred urology (urethritis, for example) or sexually transmission (gonorrhea, chlamydia, etc. ) of the disease: there is also a hidden presence of these diseases, whose result becomes prostatitis;
- regular stool problems (more often chronic constipation);
- The use of spicy, smoked and retaining foods, alcohol and other products can also cause inflammation of the prostate gland
- Other factors that cause impaired immunity: excessive loads, multiple or long stress.
Prostatitis: Consequences
In case of premature appeal to the urologist, acute bacterial prostatitis can lead to the formation of an abscess and prostate gland edema, which is capable of not only complicating urination, but to make it completely impossible.
The latter, such as inflammation, can cause severe body intoxication, characterized, among other things, by a sharp increase at a temperature of up to 40-41 ° C (with sharp temperature fluctuations to 1 degree).
However, most of the time complications of this type can be avoided, as prostatitis manifestations of this species usually force the patient not to delay the visit to a specialist.
In the case of a chronic way of the disease, whose symptoms are not so pronounced, the development of proper and timely complications is quite possible. Without the appropriate drug and therapeutic effect, inflammation can spread to other organs of the genitourinary system, which can lead to development:
- Cystitis - Bladder inflammation;
- Pyelonephritis - renal inflammation;
- vesiculitis - inflammation of seed bubbles;
- Inflammation of the testicles and appendages of the testicles.
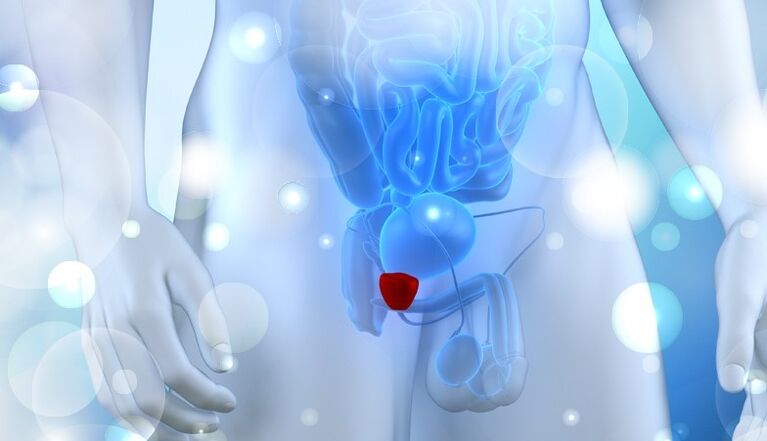
It should be remembered that inflammation of eggs and testicles is one of the most common complications and can cause male infertility, which, in turn, is treated for a long time, difficult and not always successful; Therefore, faster treat prostatitis, more likely to avoid complications of this type.
In some cases, the consequence of chronic prostatitis may be its transition to a form of calculation. Prostatitis of calculation is characterized by the formation of calculations (small pebbles) in the gland excavating ducts, to get rid of which is very medicine.
In addition, the cause of prostatitis is a hormonal failure caused by insufficient production of hormones with sexual glands.
The development of prostatitis is facilitated by various causes. Often signs of prostatitis manifest themselves in those men who perform irregular sex life, usually suffer hypothermia and injuries.
In addition, prostatitis can develop as a result of a decrease in immunity, worsening blood flow and lymphatic circulation in men of the small pelvis of man, as a result of a hormonal failure, which causes a certain level of androgynous failure.
A factor that contributes to the manifestation of prostatitis is also considered several sexually transmitted infections. Therefore, prostatitis often manifests in men after unprotected sex.
There are 4 main forms of prostatitis: acute bacterial prostatitis, chronic bacterial prostatitis, non -bacterial prostatitis and prostatinia.
In people under 35, the disease usually continues in the form of acute bacterial prostatitis. Bacterial prostatitis is called when laboratory confirmation of the presence of infection.
Most of the time, it turns out to be chlamydia, trichomoniasis, gardnerelos or gonorrhea. The infection enters the prostate gland of the urethra, bladder, straight, through the blood and lymphatic vessels of the pelvis.
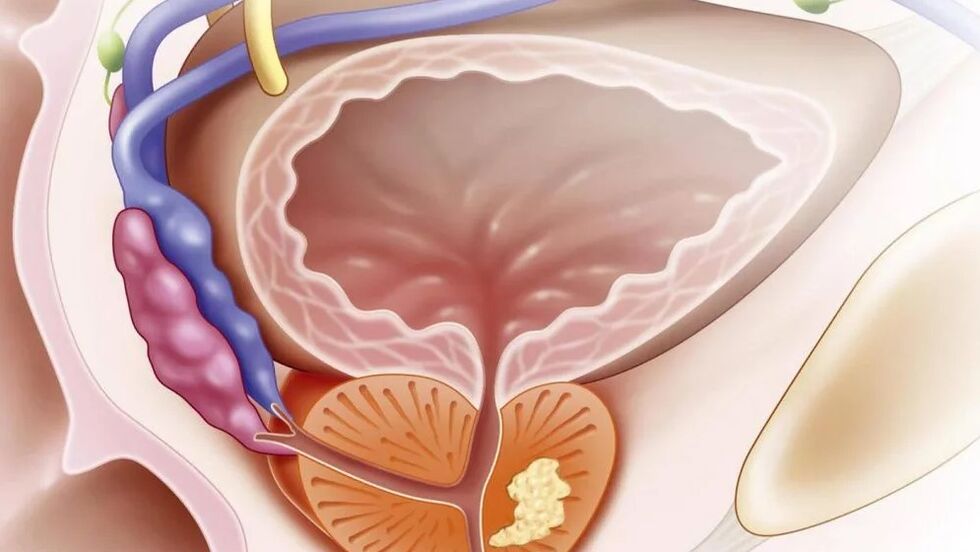
However, recent studies prove that, in most cases, the infection is in layers of existing disorders in the structure of prostate tissue and blood circulation in it. With non -bacterial prostatitis, bacteria cannot be isolated, although this does not exclude their presence.
In older patients, chronic forms of the disease are diagnosed more often. Prostatodynia is called a clinical image of prostatitis, a prostate tissue seal with no signs of its inflammation.
Classification
According to the criteria of the US National Institute of Health (NIH USA), four categories of prostatitis are distinguished from 1995:
- Acute Prostatitis (Bacterial)
- Chronic bacterial prostatitis
- Non -Bacterial Prostatitis Chronic / Chronic Pelvic Pain (CP / CPPS)
- Chronic inflammatory pelvic pain syndrome (leukocytes are determined in the secret of prostate, urine and ejaculated)
- Non -inflammatory chronic pelvic pain syndrome, in which signs of inflammation are absent
- Asymptomatic chronic prostatitis
Currently, an international classification of prostatitis has been adopted, which is the most complete and covering all types of inflammation:
- Category I. Acute prostatitis;
- Category II. Bacterial of chronic prostatitis;
- Category III. Chronic nebacterial prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome is a disease in which an infection that lasts more than 3 months is not detected;
Subcategory III A. Chronic inflammatory pelvic pain syndrome (leukocytes are determined in the secret of the prostate);
Subcategory III B. Non -inflammatory pelvic pain syndrome (there are no leukocytes in the prostate secret); - Category IV. Procedure for lurked chronic prostatitis (leukocytes are present at the prostate secret, the patient does not complain, the disease is detected by chance).
The treatment of prostatitis varies depending on the form of the disease occurs in a man. Therefore, bacterial prostatitis can occur in both acute form and a chronic disease.
Often non -bacterial prostatitis is also diagnosed as a chronic disease. This variety of prostatitis is also called chronic pelvic pain syndrome.
In these patients, all characteristic symptoms of prostatitis are observed, but there are no bacteria in the prostate secret.
Acute bacterial prostatitis is characterized by rapid development. At the same time, a person suffers from intense pain, there are signs of general poisoning. The symptoms in the chronic form of the disease are much less clearly manifested. In this case, the disease manifests itself gradually.
And if the course of prostatitis in the acute way, as a rule, ends with the complete healing of the disease, then with chronic prostatitis, relapses appear quite often. This should be taken into consideration in the treatment of prostatitis at home. In addition, in the presence of inflamed stones in the prostate gland, disease therapy is a more complex process.
With non -bacterial prostatitis (chronic pelvic pain), a person develops serious pain located in the pelvic, genitals and perineum area. There are no signs of inflammation in the prostate.
This disease is common among modern men of different age groups, but most of the time the disease affects people from 35 to 45 years. To this day, experts express various assumptions about what are the causes of this form of prostatitis.
Therefore, there is a theory that this syndrome causes damage to the tissues of a bacterial prostate. In addition, there is an opinion that the disease manifests itself due to the fall of urine in the prostate gland.
As we said, the acute and chronic disease course is possible. In this case, the appearance of acute prostatitis is more often caused by gram-negative bacteria.
This form of the disease is relatively easy to diagnose and treat antibiotics. At the same time, cases of chronic non -bacterial prostatitis are often found among men, which is more difficult to diagnose and has no connection with a certain infectious injury.
Therefore, in the case of chronic prostatitis, antibiotic treatment will not be able to give the proper effect. According to statistics, about 35% of men over fifty years of chronic prostatitis.
Chronic and acute prostatitis treatment
In the case of signs of prostatitis, acute and chronic, you should consult a urologist, who will establish what type of diagnosis occurs and will also help heal the disease and strengthen the body as a whole. It should be remembered that this applies equally to both types of prostatitis, each of which can lead to its complications.
Primary reception
The primary reception of an expert involves research and examination of the patient (including rectal, which allows to determine the degree and nature of increased prostate gland), as well as the appointment of the necessary tests and other diagnostic measures.
The first and important sign of prostatitis is the impaired urination that causes discomfort. Another sign of the disease is rapid urination, but in which urine comes out in small portions.
Acute symptoms of the disease

The disease is suddenly formed and is characterized by pronounced manifestations.
- frequent painful urination;
- pain during defecation;
- impaired power;
- groin pain, the sacred area and the anus;
- High sweating;
- fatigue.
Each male body is individual and symptoms can manifest separately, or all at once.
Signs in a chronic way of the disease
Chronic prostatitis is generally characterized by the same signs, however, it continues with less pronounced symptoms.
In addition, the following manifestations can be observed:
- greater irritability;
- a feeling of overflowing bladder;
- deterioration of quality or lack of orgasm;
- Selection during defecation of the urethra.
The first signs of prostatitis, which a man should definitely pay attention and get in touch with the urologist:
- Intense pain during urination. At the end of the process, an unpleasant burning sensation is felt.
- Improving body temperature.
- The feeling of not completely emptying the bladder.
- Discomfort in the groin and groin area.
- Insufficient jet pressure while visiting the bathroom.
The treatment of prostatitis is performed, depending on the form of the disease. Acute inflammation is an indication for patient hospitalization in the urological hospital, with chronic patients undergo the course of home therapy. If the cause of the disease was a sexually transmitted infection, both partners should take antibiotics.
In the treatment of acute prostatitis, it is important that systemic antibacterial treatment is important.

The main drug groups include:
- Antibiotics. Used in the form of tablets, capsules, candles, syrups and other types.
- Anti -inflammatory drugs.
- Spasmalgotic and painkillers.
- Preparations to increase immunity.
- Vitamins.
- Antitrass medicines.
Massage
This procedure is one of the most effective methods for the treatment of prostatitis. Thanks to her, accumulated in the prostate gland, the secret is squeezed and then removed independently by the urethra. In addition, prostate massage helps improve blood supply in gland tissue, which increases the efficacy of antibacterial and local therapy.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic treatment helps improve prostate gland tissue trophicism and accelerate the recovery process. The following methods of physical therapy are possible:
- Microwave transtors,
- Diadinamoforesis,
- laser therapy,
- Ultrasonic phonophoresis.
Exercise
The main signs of the disease
A disease like prostatitis in most men develops suddenly. In the patient, the temperature increases markedly, a feeling of weakness, the fever appears. The main sign of inflammation of the prostate is intense perineum pain, which gives the pubic area, anal opening, sacred. During urination, defecation and with any other tension of the pelvic muscles, the pain increases.